Difference between revisions of "Mud Tongue"
From World of Entorais Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search (layout) |
m (layout) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
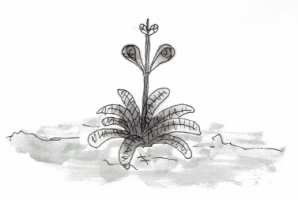
[[File:Mud_tongue.png|thumb|right|x200px|''Mud Tongue'' - Sebastian Romu © 2018]] | [[File:Mud_tongue.png|thumb|right|x200px|''Mud Tongue'' - Sebastian Romu © 2018]] | ||
= | ==About== | ||
;Common Names:Mud Tongue | ;Common Names:Mud Tongue | ||
;Classification:Herbaceous, Flower | ;Classification:Herbaceous, Flower | ||
;Description | |||
:A common leafy plant of the [[Waejiran Plateau]] with a soft, velvety surface to its leaves, and pairs of whorled long petalled flowers on a reedy central stem. The mud tongue is so named for the mud-like taste of its leaves, which make an excellent bitter. The flowers see some use as a vasoconstrictor. | :A common leafy plant of the [[Waejiran Plateau]] with a soft, velvety surface to its leaves, and pairs of whorled long petalled flowers on a reedy central stem. The mud tongue is so named for the mud-like taste of its leaves, which make an excellent bitter. The flowers see some use as a vasoconstrictor. | ||
=Ecology= | ==Ecology== | ||
;Rarity:Common | ;Rarity:Common | ||
;Distribution:Sub-tropical savanna | ;Distribution:Sub-tropical savanna | ||
;Life Cycle:Annual, flowering mid summer, to produce seeds dispersed by wind in early autumn. | ;Life Cycle:Annual, flowering mid summer, to produce seeds dispersed by wind in early autumn. | ||
=Uses= | ==Uses== | ||
;Cultivation:wild | ;Cultivation:wild | ||
;Culinary:bitter (leaves) | ;Culinary:bitter (leaves) | ||
| Line 16: | Line 17: | ||
;Other:<!-- other uses--> | ;Other:<!-- other uses--> | ||
=Culture= | ==Culture== | ||
<!-- unique cultural notes--> | <!-- unique cultural notes--> | ||
=Stories= | ==Stories== | ||
<div style="column-count:3;-moz-column-count:3;-webkit-column-count:3"> | |||
</div> | |||
=See Also= | ==See Also== | ||
[[Category:Flora]] | [[Category:Flora]] | ||
Revision as of 21:47, 5 February 2020
About
- Common Names
- Mud Tongue
- Classification
- Herbaceous, Flower
- Description
- A common leafy plant of the Waejiran Plateau with a soft, velvety surface to its leaves, and pairs of whorled long petalled flowers on a reedy central stem. The mud tongue is so named for the mud-like taste of its leaves, which make an excellent bitter. The flowers see some use as a vasoconstrictor.
Ecology
- Rarity
- Common
- Distribution
- Sub-tropical savanna
- Life Cycle
- Annual, flowering mid summer, to produce seeds dispersed by wind in early autumn.
Uses
- Cultivation
- wild
- Culinary
- bitter (leaves)
- Medicinal
- vasoconstrictor (flowers)
- Other